Biofeedback, a clinically proven practice, known to improve our capacity to consciously influence involuntary biological processes. This approach entails delivering feedback on certain biological processes in order to increase awareness and control over one’s physiology. For example, we’re only partly aware of our heart rate; noticing it mainly under cardiac arrhythmia or hyperventilation. If, however, the heart rate is recorded and the signal is transformed into sounds or visuals, then the physiological process is tangibly visible. In the sphere of art, biofeedback becomes a tool for self-awareness and regulation, allowing artists to tap into their underlying physiological states for inspiration.
” Biofeedback in art transforms intuition into tangible guide ” Said the well-established psychologist Dr. Emma Seppala.
Stressing on the significance of biofeedback roll in boosting creative expression. This approach increases self-understanding and emotional/physical regulation. This article taps into biofeedback practices as a tool for skill perfection and mind-body equilibrium.

What is Biofeedback ?
Individuals use biofeedback, a scientifically proven practice, in which people learn to regulate physiological processes that are generally automatic, such as heart rate or muscular tension. Monitors attached to the body measure these functions and offer real-time data. This feedback allows individuals to become more aware of their internal processes, they gradually learn to control these functions voluntarily. Biofeedback has been successfully used to manage, stress, anxiety, and physical pain.
Wearable technology has made self-conducted biofeedback more accessible, enabling individuals to keep track of their physiological states and practice self-regulation in a tangible manner.
Biofeedback in Art
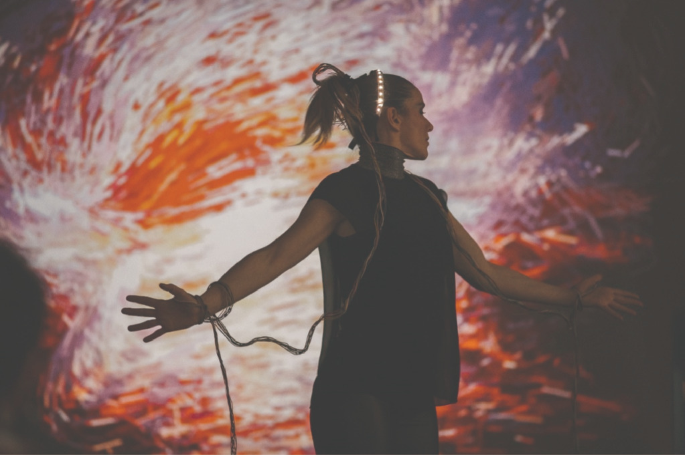
Biofeedback in art entails artists shaping and directing their creative process through the use of physiological data such as heart rate or brainwaves patterns. Artists wear sensors that measure their bodily responses as they create. Real-time visualization of data allows artists to examine how their physical and emotional conditions interact with their creative process.
Biofeedback in art varies widely. it can include simple heart rate data altering a digital art piece in terms of color or shape. Or, complex EEG systems might change performance soundscape based on brainwaves.
Constant innovation marks this field, artists experiment with VR and AR technologies, generating captive biofeedback art experiences. Meanwhile, some novel artists explore using artificial intelligence to examine data for deeper insights into the inner curves of the creative process.
Biofeedback can be practiced in mild forms. For example artists who pay close attention to their physical responses, may sense a tense grip on their brush or other tools, thereby relaxing their hand. This awareness promotes a calm and focus stream of creativity.
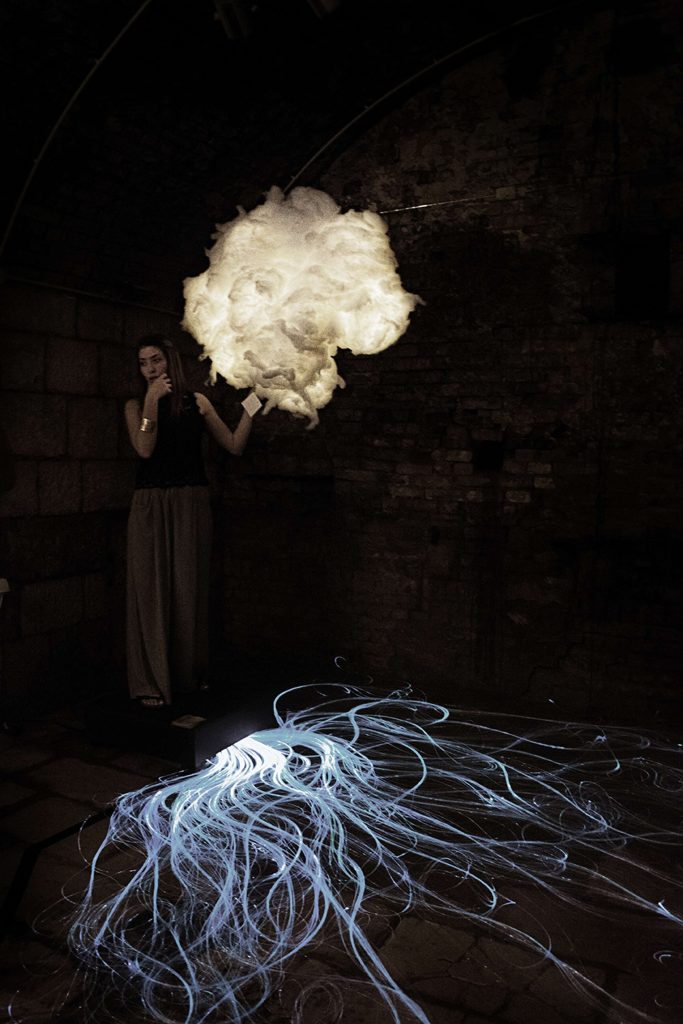

How Does Biofeedback Enhance the Creative Process ?
Biofeedback boosts the creative process in plenty of ways:
Enhanced Focus: Artists can spot stress responses through physiological cues, such as heart rate, leading to deeper concentration.
Emotional Awareness: Artists obtain insights into their emotional state, which allows them to funnel their emotions more efficiently.
Physical Relaxation: Spotting signals of physical tension allows creators to relax, reducing restlessness and maintaining a stable hand or posture.
Creative Experimentation: Physiological data may become an integral part of the art it self, stimulating new ideas and experiments.
Stress Reduction: Habitual use of biofeedback techniques restricts stress , producing a calm frame of mind that promotes creativity and flow.
Pioneers of Biofeedback Art
Biofeedback art, in which artists use physiological cues to guide and influence their work, is a growing discipline with various key contributors. For example, in her piece “Wave UFO” renown artist Mariko Mori employed EEG (electroencephalography), to exhibit brainwaves of participants in real-time, producing an immersive experience.
Rafael Lozano-Hemmer designed “Pulse Room” an installation in which light bulbs flashed in sync with participants’ heartbeats. Among others, these artists are pioneering the use of biofeedback in the creation of art, demonstrating new and novel ways in which technology, physiology and art intersect, to create extremely personal and interactive art experiences.







