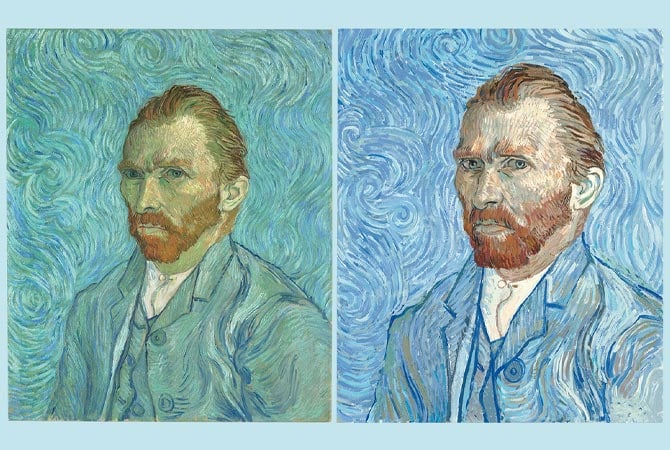
Art forgeries stand out as a sophisticated interplay of talent and deception in the intriguing domain of the art world. These highly skilled forgeries bring into question our assumptions of authenticity and value in art. This article delves into the intricate realm of art forgeries. It sheds light on the forgers’ motives and their impact on the art market. Additionally, it highlights the increasing role of technology in unveiling these masterful deceptions. By evaluating these traits, we obtain knowledge concerning a mysterious yet captivating area of art history.
The Art of Deception: An overview
Art forgeries are the creation and selling works of art that are fraudulently ascribed to famous artists. This deceitful method to transforming a lesser-known work into a masterpiece. The motives behind these forgeries vary; they are mostly driven by financial gain, but they can also be motivated by the pleasure of deception to criticize the art establishment.
The Psychology of the Forger:
Forgers are frequently talented painters in their own right, with a thorough grasp of the approaches and aesthetics of the artists they copy. Their ability to successfully imitate these styles demonstrates their artistic prowess. Nonetheless, some chose the route of trickery, whether out of a desire for notoriety, financial desperation, or a type of revolt against the art world’s elitism.
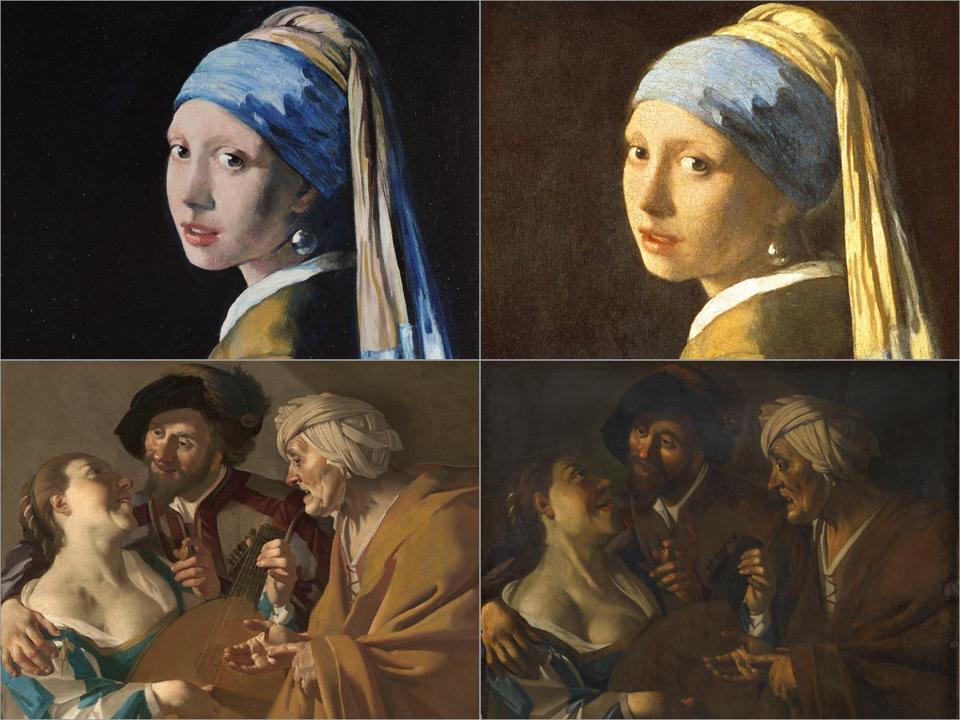

Famous Forgeries: Han Van Meegeren
Han Van Meegeren, a Dutch painter who falsified Vermeer paintings, is one of the best-known and most notable forgers in art history. Van Meegeren actively forged ‘The Supper at Emmaus’, which experts praised as a masterpiece. his persuasive skills led top experts to support his forgeries, until an astonishing trial in the 1940s exposed them.
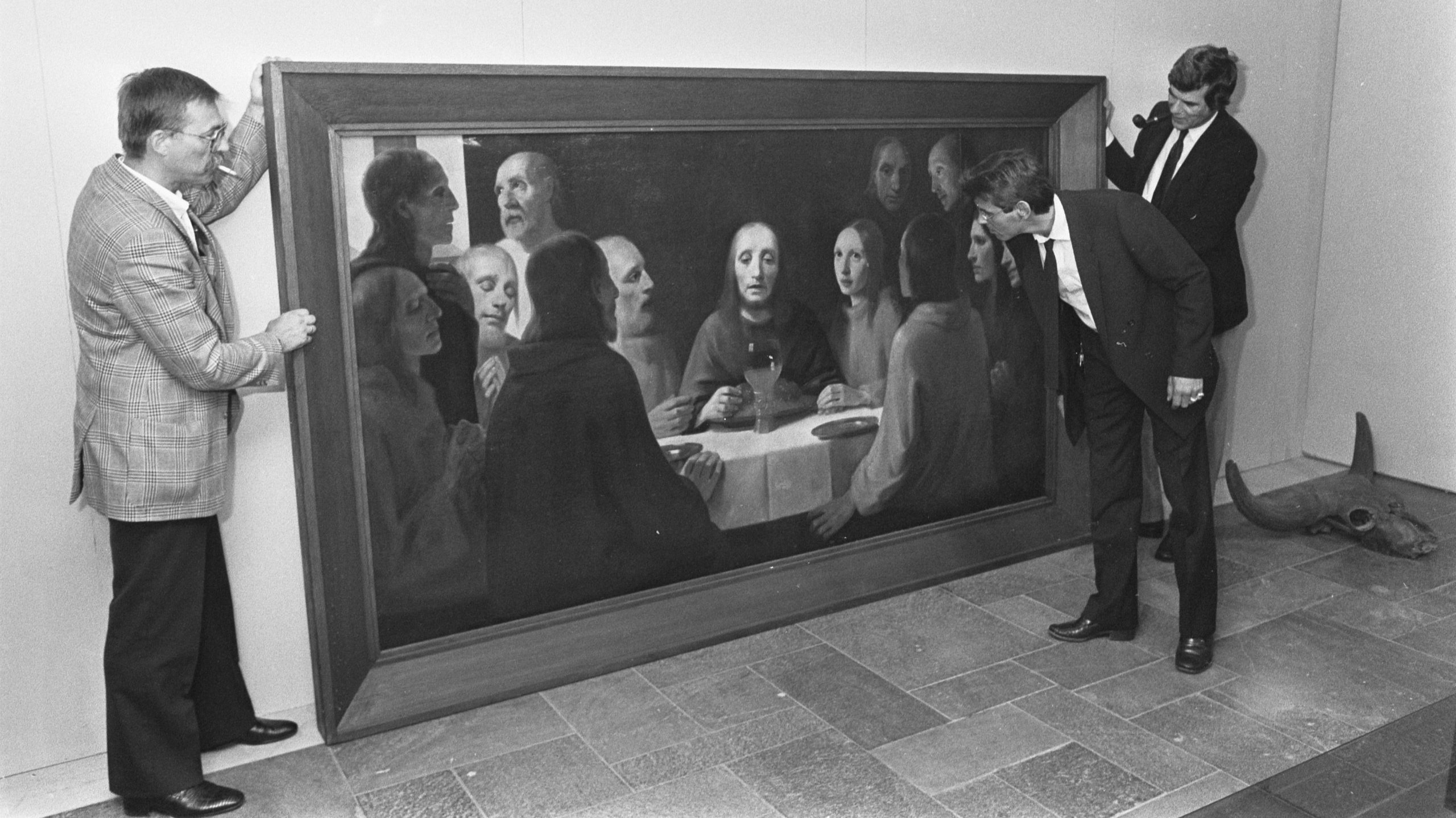

Wolfgang Beltracchi: A Modern Master Forger
In the twenty-first century, Wolfgang Beltracchi was held accountable for one of the most notable art forgeries in recent history. He falsified artworks for 40 years, passing them off as unknown works by early twentieth-century painters. Beltracchi’s case emphasized the flaws in the art authentication procedure.
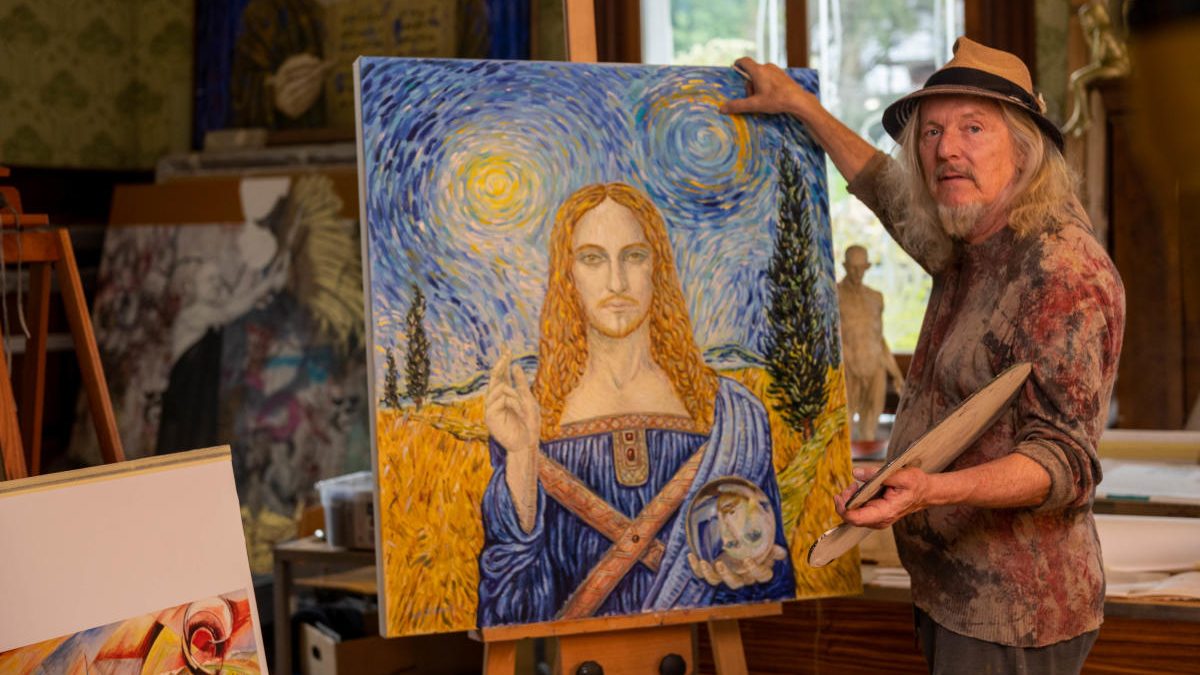

The Role of Technology in Detecting Forgeries
As art forgery methods get increasingly complex, so do detecting policies. High-resolution imaging and chemical evaluation have become indispensable tools in the authenticity of artworks. These technologies may detect irregularities that are not evident to the human eye, assisting professionals in determining the real origins of a piece.
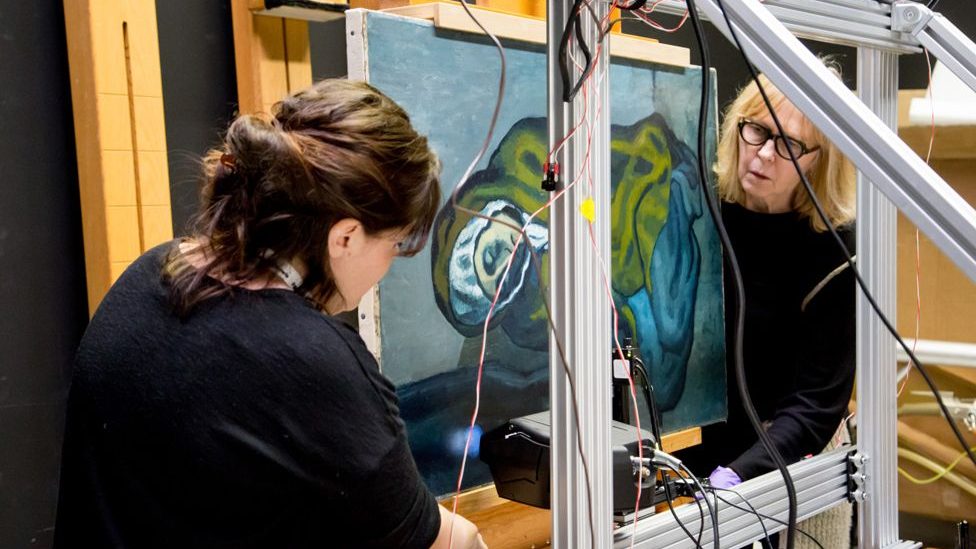

The impact on the Art Market
The presence of forgeries has tremendous effects on the art market. It creates a broad sense of distrust, which has an impact on pricing and the legitimacy of artworks. Art collectors and institutions are becoming more cautious, frequently depending on provenance and detailed histories of artworks to determine their validity.
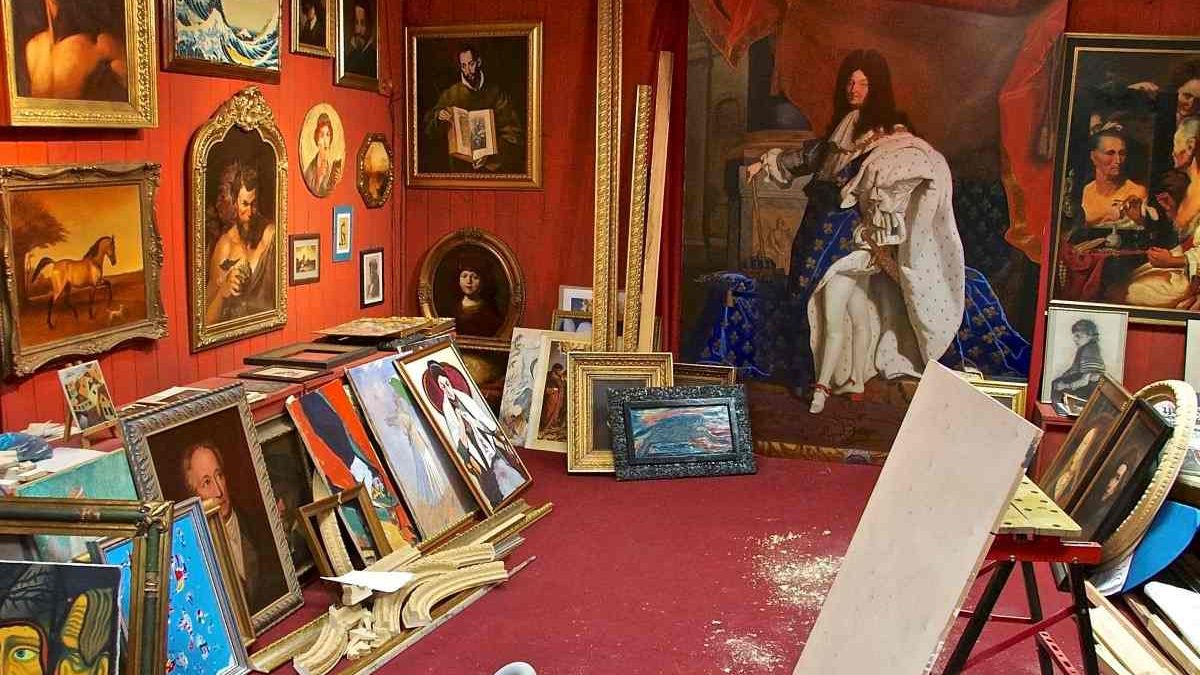

The Enduring Fascination with Art Forgeries
Despite the drawbacks, art forgeries continue to pique people’s interest. Art forgeries raise questions about the value of original works versus skilled imitations. They challenge our understanding of art and authenticity. Additionally, they highlight the subjective nature of art assessment. Forgeries reveal the complex relationship between art, its value, and authenticity.
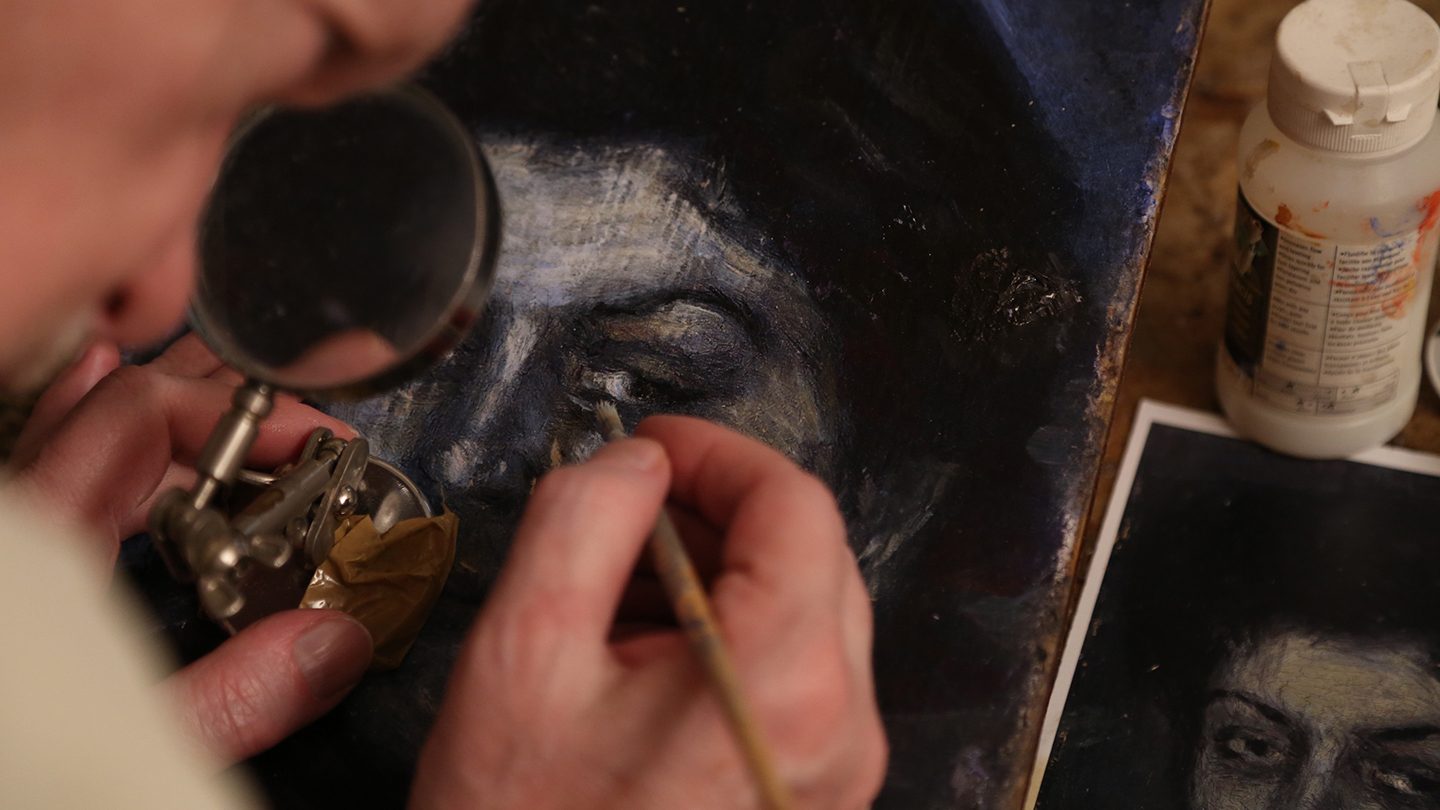

To summarize, art forgeries are an intricate combination of ingenuity and deception that challenges our conceptions of authenticity and value in the art world. From Van Meegeren to Beltracchi, these instances demonstrate the delicate line between creative talent and criminal cleverness. They also highlight the expanding importance of technology in artwork authentication, giving scientific precision to the art of detection. The art world grapples with the possible repercussions of forgeries. These captivating narratives serve as cautionary tales as well as observations on the subjective nature of art itself. This remarkable facet of art history reminds us of the delicate dance between reality, perception, and the persistent fascination of masterpieces, whether genuine or expertly created.







